

Environmental Exposures: Fluoride, Retinal, Vitamin A Toxcicity.Chronic Medication Use: Isotretinoin, Etretinate, Acitretin, Retinoids.
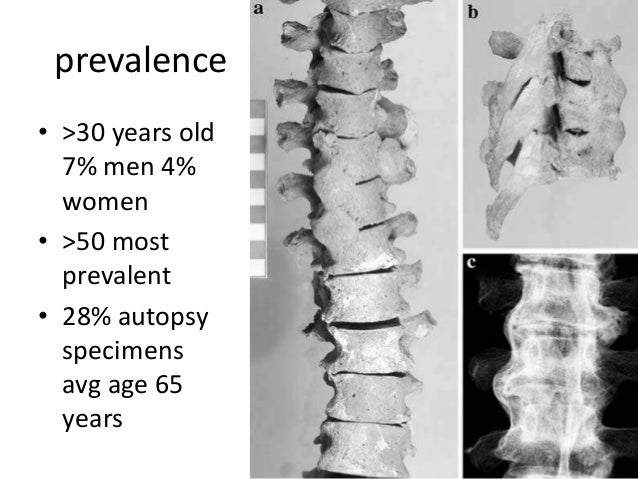
There are certain factors that have come to be associated with DISH and are thought to have some relation to the pathophysiology behind the disease process. A number of theories have been postulated that relate abnormal growth and function of osteoblasts in the osteoligamentous binding centers that however, this is not a widely accepted theory among the current research. The current research on DISH lacks a definitive cause of the disease. Spur formation in appendicular skeleton seen at the olecranon process, patellar ligament, and calcaneus.Enthesopathies, which is a disorder involving attachment of tendon or ligament to bone at the entheses, are commonly seen in the iliac crest, ischial tuberosity, and greater trochanters.No inflammation at sacroiliac joint or facet joint ankylosis.Flowing ossification along the anterior or right anterolateral aspects of at least 4 consecutive vertebrae.Specific features shown either through a radiograph, MRI, or CT scan in patients who are diagnosed with DISH could include a few of the following and not all are required to be seen to have the diagnosis of DISH Absence of apophyseal joint degeneration or SI inflammatory changes.Ī formal diagnosis of DISH does not require or mandate the presence of constitutional and metabolic abnormalities however, it is known through numerous studies that systemic conditions are associated with DISH in varying degrees.Preservation of intervertebral disc spaces.Anterolateral ossifications of at least 4 contiguous thoracic segments.The most commonly used classification criteria to diagnose DISH was designed by Resnick and Niwayama in 1976 and includes the following : The following medications have been used as a method of control and/or manage the symptoms of the disease process. Ĭurrent research does not outline a specific and definitive schedule of medications used to treat DISH.
 Neurological impairments, while typically uncommon with the presentation of this disease, can manifest in the form of spinal cord compression, muscle weakness, numbness and tingling, and sesory loss. Cardiovascular conditions including, but not limited to hypertension, atrial fibrillation, left ventricular hypertrophy, peripheral arterial disease, and cardiovascular disease. The following conditions are shown to be commonly associated with the diagnosis of DISH across the spectrum of individuals affected. One of the most prevalent associations according to recent research is to metabolic syndromes. Decreased ROM - Primarily in the Axial Skeleton or Peripheral JointsĪssociated Co-morbidities ĭISH has been shown to have a multiple associations with a number of conditions and dysfunctions. Other symptoms can include, but are not limited to the following characteristics : These characteristics are typically attributed to altered biomechanics of the axial skeleton that lead to pain and decreased mobility. However, due to the varying manifestations and differing locations of the characteristics of the disease, a number of characteristics can be seen in clinical presentations. Ĭharacteristics/Clinical Presentation ĭISH has been found to be present asymptomatically in most clinical cases. It has also been discussed throughout the research that a genetic component has a possible place in the role of development and diagnosis of the disease. Other structures commonly affected include: pelvis, patella, calcaneus, and the olecranon. DISH is found to affect the axial skeleton with the thoracic spine (T7-T11), being the most common levels affected. The recent evidence of DISH reports prevalence of the disease is increased in with increasing age more prominently found in the 60s and 70s. One of the main reasons for this variability is the different locations of structural manifestations in the vertebral column. The reported prevalence of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis is widely varied throughout the course of available research. DISH is a complex disorder that not only affects the musculoskeletal system, but also can cause additional gastrointestinal, respiratory, cardiovascular, and neurological impairments due to bone compression of adjacent structures. DISH primarily affects the Anterior Longitudinal Ligament (ALL) at the attachment sites to bone in the vertebral column. Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) refers to a non-inflammatory disease that is characterized by ossification/calcification of soft tissues, entheses, and spinal ligaments.
Neurological impairments, while typically uncommon with the presentation of this disease, can manifest in the form of spinal cord compression, muscle weakness, numbness and tingling, and sesory loss. Cardiovascular conditions including, but not limited to hypertension, atrial fibrillation, left ventricular hypertrophy, peripheral arterial disease, and cardiovascular disease. The following conditions are shown to be commonly associated with the diagnosis of DISH across the spectrum of individuals affected. One of the most prevalent associations according to recent research is to metabolic syndromes. Decreased ROM - Primarily in the Axial Skeleton or Peripheral JointsĪssociated Co-morbidities ĭISH has been shown to have a multiple associations with a number of conditions and dysfunctions. Other symptoms can include, but are not limited to the following characteristics : These characteristics are typically attributed to altered biomechanics of the axial skeleton that lead to pain and decreased mobility. However, due to the varying manifestations and differing locations of the characteristics of the disease, a number of characteristics can be seen in clinical presentations. Ĭharacteristics/Clinical Presentation ĭISH has been found to be present asymptomatically in most clinical cases. It has also been discussed throughout the research that a genetic component has a possible place in the role of development and diagnosis of the disease. Other structures commonly affected include: pelvis, patella, calcaneus, and the olecranon. DISH is found to affect the axial skeleton with the thoracic spine (T7-T11), being the most common levels affected. The recent evidence of DISH reports prevalence of the disease is increased in with increasing age more prominently found in the 60s and 70s. One of the main reasons for this variability is the different locations of structural manifestations in the vertebral column. The reported prevalence of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis is widely varied throughout the course of available research. DISH is a complex disorder that not only affects the musculoskeletal system, but also can cause additional gastrointestinal, respiratory, cardiovascular, and neurological impairments due to bone compression of adjacent structures. DISH primarily affects the Anterior Longitudinal Ligament (ALL) at the attachment sites to bone in the vertebral column. Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) refers to a non-inflammatory disease that is characterized by ossification/calcification of soft tissues, entheses, and spinal ligaments.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
